

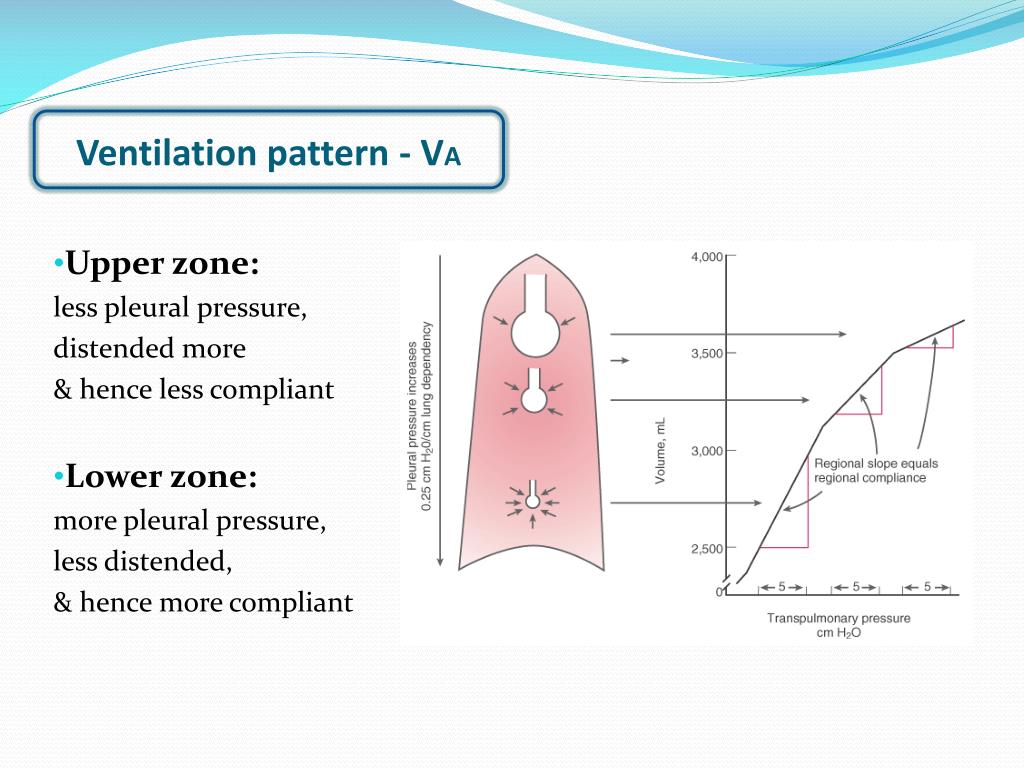
Resting physiologic dead space (VD), and physiologic dead space to tidal volume ratio (VD/VT), may be a better predictor of PPC than PETCO 2. However, breath-breath breathing pattern significantly affects PETCO 2. Recently, resting end-tidal partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PETCO 2) has been shown as a good predictor for increased risk of PPC. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) is performed to predict risk of PPC in patients with severely reduced predicted postoperative forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) and diffusion of carbon monoxide (DLCO). Lung resection surgery carries significant risks of postoperative pulmonary complications (PPC). 3The Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Torrance, CA, United States.2Department of Medicine, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, VA Long Beach Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA, United States.1Department of Medicine, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of California, Irvine, CA, United States.Church 1 Amir Abolhoda 1,2 Janos Porszasz 3 Catherine S. Positive pressure ventilation (i.e.Rohit Godbole 1 Sanford B.Neck extension and jaw protrusion (can increase it twofold).General anesthesia – multifactorial, including loss of skeletal muscle tone and bronchoconstrictor tone.The ratio of physiologic dead space to tidal volume is usually about 1/3. Alveolar dead space is the volume of gas within unperfused alveoli (and thus not participating in gas exchange either) it is usually negligible in the healthy, awake patient.
Anatomic dead space is the volume of gas within the conducting zone (as opposed to the transitional and respiratory zones) and includes the trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, and terminal bronchioles it is approximately 2 mL/kg in the upright position.

Physiologic or total dead space is the sum of anatomic dead space and alveolar dead space. Dead space is the volume of a breath that does not participate in gas exchange.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
